google Chrome / Firefox shortcut key
ctrl + shift + delete -> This will bring Clear browsing data
ctrl + shift + delete -> This will bring Clear browsing data
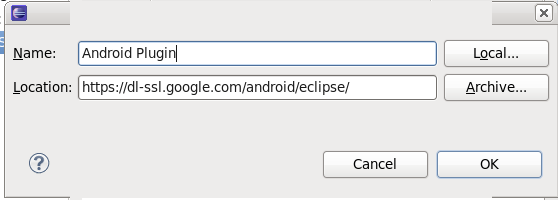
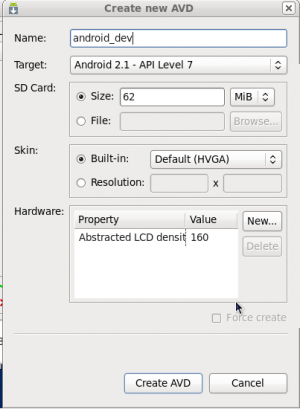
.apk file that you install onto a device. They contain things such as application source code and resource files. Some are generated for you by default, while others should be created if required. The following directories and files comprise an Android project:src/src/your/package/namespace/ActivityName.java. All other source code files (such as .java or .aidl files) go here as well.bin.apk file and other compiled resources.jnigen/R.java file and interfaces created from AIDL files.assets/.apk file as-is, and the original filename is preserved. You can navigate this directory in the same way as a typical file system using URIs and read files as a stream of bytes using the theAssetManager. For example, this is a good location for textures and game data.res/anim/color/drawable/layout/menu/raw/assets/ directory only differs in the way that you access them. These files are processed by aapt and must be referenced from the application using a resource identifier in the R class. For example, this is a good place for media, such as MP3 or Ogg files.values/res/ directory, resources written to XML files in this folder are not referenced by the file name. Instead, the XML element type controls how the resources is defined within them are placed into the R class.xml/PreferenceScreen,AppWidgetProviderInfo, or Searchability Metadata. See Application Resources for more information about configuring these application components.libs/AndroidManifest.xmlproject.propertieshttps://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/
yum install glibc.i686 glibc-devel.i686 libstdc++.i686 zlib-devel.i686 ncurses-devel.i686 libX11-devel.i686 libXrender.i686 libXrandr.i686

package com.gubs.android;
import android.app.Activity;import android.os.Bundle;import android.widget.TextView;
public class GubsFirstSampleAndroidApp extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); TextView tv = new TextView(this); tv.setText("Hello Android..Its Gubs and my first App"); setContentView(tv); }}ALTER TABLE contacts ADD email VARCHAR(60) AFTER name;ALTER TABLE contacts ADD email VARCHAR(60) FIRST;CREATE USER 'username'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password123'
| MySQL Type Name | Return value ofGetColumnClassName | Returned as Java Class |
|---|---|---|
| BIT(1) (new in MySQL-5.0) | BIT | java.lang.Boolean |
| BIT( > 1) (new in MySQL-5.0) | BIT | byte[] |
| TINYINT | TINYINT | java.lang.Boolean if the configuration property tinyInt1isBit is set to true (the default) and the storage size is 1, or java.lang.Integer if not. |
| BOOL, BOOLEAN | TINYINT | See TINYINT, above as these are aliases for TINYINT(1), currently. |
| SMALLINT[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | SMALLINT [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Integer (regardless if UNSIGNED or not) |
| MEDIUMINT[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | MEDIUMINT [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Integer, if UNSIGNED java.lang.Long (C/J 3.1 and earlier), or java.lang.Integer for C/J 5.0 and later |
| INT,INTEGER[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | INTEGER [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Integer, if UNSIGNED java.lang.Long |
| BIGINT[(M)] [UNSIGNED] | BIGINT [UNSIGNED] | java.lang.Long, if UNSIGNED java.math.BigInteger |
| FLOAT[(M,D)] | FLOAT | java.lang.Float |
| DOUBLE[(M,B)] | DOUBLE | java.lang.Double |
| DECIMAL[(M[,D])] | DECIMAL | java.math.BigDecimal |
| DATE | DATE | java.sql.Date |
| DATETIME | DATETIME | java.sql.Timestamp |
| TIMESTAMP[(M)] | TIMESTAMP | java.sql.Timestamp |
| TIME | TIME | java.sql.Time |
| YEAR[(2|4)] | YEAR | If yearIsDateType configuration property is set to false, then the returned object type is java.sql.Short. If set to true (the default) then an object of type java.sql.Date (with the date set to January 1st, at midnight). |
| CHAR(M) | CHAR | java.lang.String (unless the character set for the column is BINARY, then byte[] is returned. |
| VARCHAR(M) [BINARY] | VARCHAR | java.lang.String (unless the character set for the column is BINARY, then byte[] is returned. |
| BINARY(M) | BINARY | byte[] |
| VARBINARY(M) | VARBINARY | byte[] |
| TINYBLOB | TINYBLOB | byte[] |
| TINYTEXT | VARCHAR | java.lang.String |
| BLOB | BLOB | byte[] |
| TEXT | VARCHAR | java.lang.String |
| MEDIUMBLOB | MEDIUMBLOB | byte[] |
| MEDIUMTEXT | VARCHAR | java.lang.String |
| LONGBLOB | LONGBLOB | byte[] |
| LONGTEXT | VARCHAR | java.lang.String |
| ENUM('value1','value2',...) | CHAR | java.lang.String |
| SET('value1','value2',...) | CHAR | java.lang.String |
Connection Properties - Miscellaneous.
These MySQL Data Types Can always be converted to these Java types CHAR, VARCHAR, BLOB, TEXT, ENUM, and SETjava.lang.String, java.io.InputStream, java.io.Reader, java.sql.Blob, java.sql.ClobFLOAT, REAL, DOUBLE PRECISION, NUMERIC, DECIMAL, TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INTEGER, BIGINTjava.lang.String, java.lang.Short, java.lang.Integer, java.lang.Long, java.lang.Double, java.math.BigDecimalDATE, TIME, DATETIME, TIMESTAMPjava.lang.String, java.sql.Date, java.sql.Timestamp